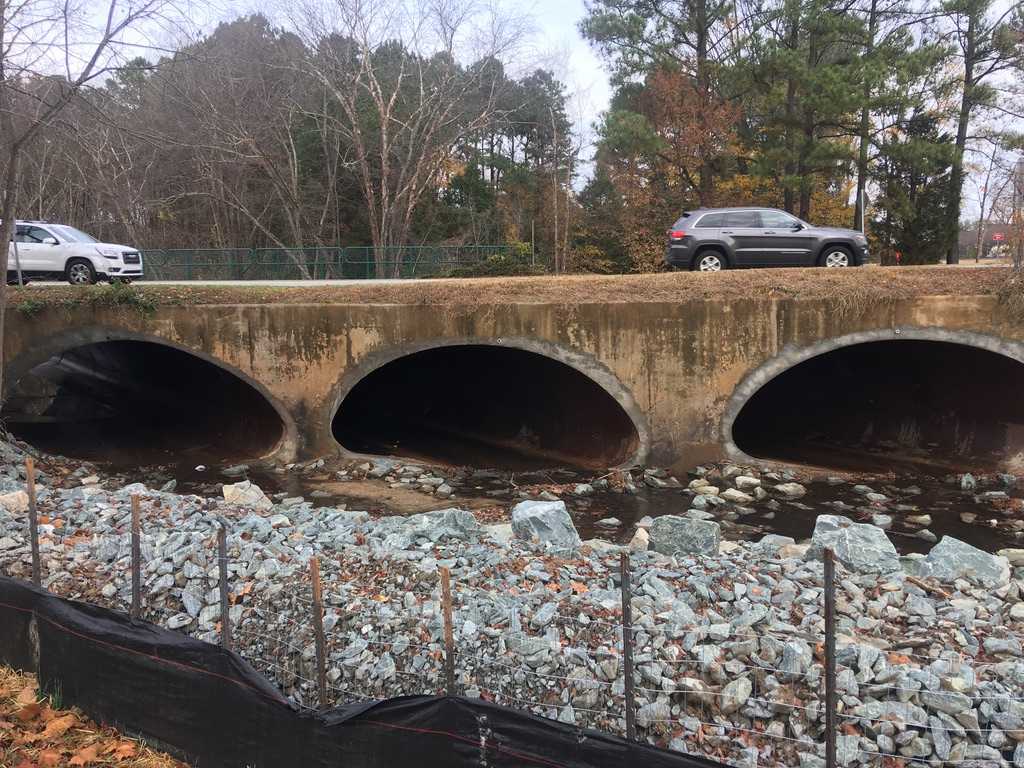
Why Is Culvert Repair Necessary?
When people hear the word “Infrastructure,” most think of roads and bridges. However, supporting those roads and bridges are countless drainage structures that can be classified as culverts. Culverts serve an unrecognized yet critical role in modern infrastructure. As a component of road and railways, culverts are designed to efficiently displace a body of water from one side of the traveling surface to the other. Maintaining culverts in proper condition, and implementing expedient repair methods, ensures that byways remain free and clear of flood hazards and stormwater runoff.
What Causes Culvert Failure or Degradation?
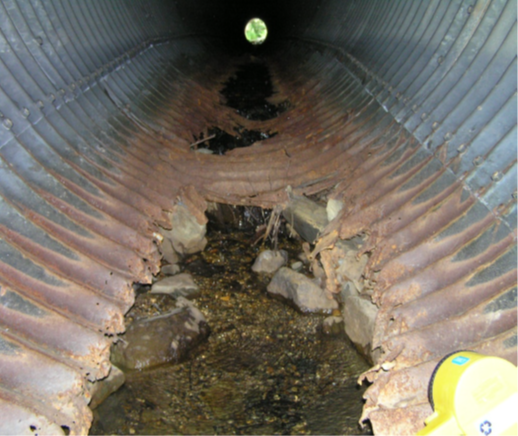
Many culverts in the ground today have served past their projected life expectancy. Commonly made out of corrugated plastic or metal, scour and abrasion have caused the culvert’s inverts to corrode and degrade over time. Without an intact invert, the culvert will begin to lose its capacity to discharge water efficiently, as the water will continue to take the path of least resistance and erode surrounding sediments and soils. This is detrimental to the structural integrity of the culvert, as corrugated culverts are designed to interact with the surrounding soils for stability.
When a culvert begins to lose its invert, two primary things can happen:
- Bedding and backfill under and around the pipe are no longer supported and are allowed to enter the stream of water, and the water washes away any material that can be dislodged.
- Because part of the circumference or “hoop” is gone, the pipe can no longer retain the soil in the position as engineered for a stable structure. This affects the structure’s ability to resist the weight above, and the circumference of the pipe begins to change – it closes in where the invert used to be and gets smaller. For these reasons, long-term structural repair methods aim to rehabilitate the entirety of the culvert barrel.
Culvert Pipe Repair Methods – Old and New
The historical methods for repairing a failing culvert called for digging up the old structure and roadway, removing the damaged culvert, and putting in new pipe. While effective, this method was time-consuming and required roads to be closed and detours erected for the replacement duration. With the advancement in trenchless repair methods, structural solutions can be accomplished with no impact to the roadway, minimal ongoing maintenance requirements, and ensure that the culvert will continue to serve its critical role for years to come.
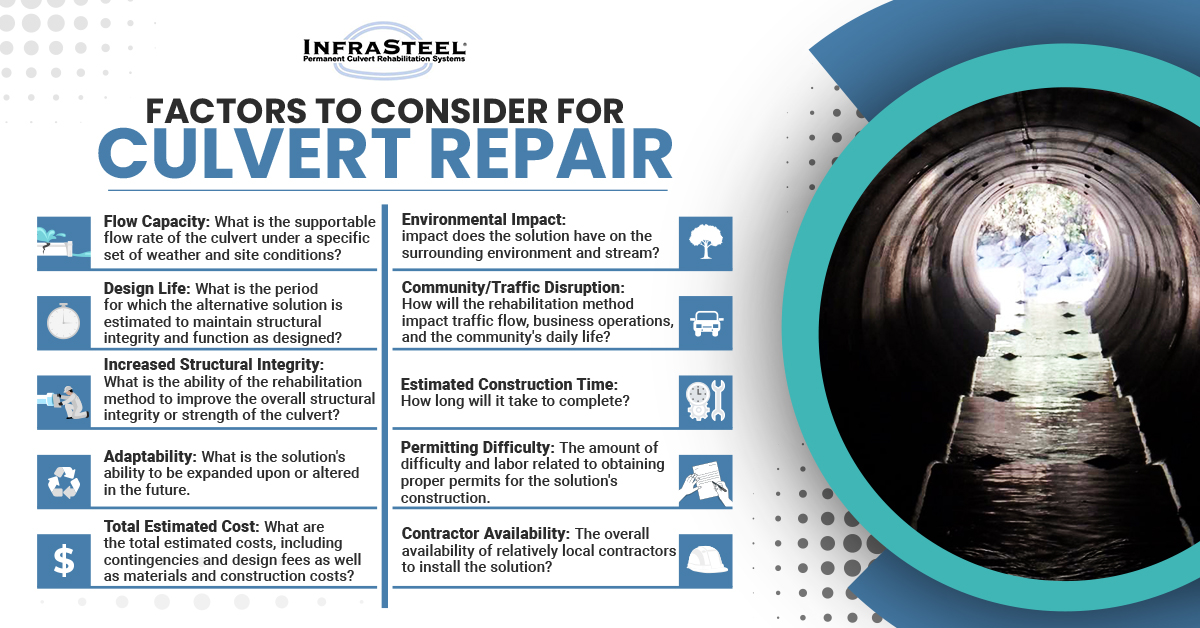
Determining The Most Effective Culvert Repair Method
To determine which repair method will be most effective, we must consider several factors.
- Flow Capacity: What is the supportable flow rate of the culvert under a specific set of weather and site conditions?
- Design Life: What is the period for which the alternative solution is estimated to maintain structural integrity and function as designed?
- Increased Structural Integrity: What is the ability of the rehabilitation method to improve the overall structural integrity or strength of the culvert?
- Adaptability: What is the solution’s ability to be expanded upon or altered in the future.
- Total Estimated Cost: What are the total estimated costs, including contingencies and design fees as well as materials and construction costs?
- Environmental Impact: What impact does the solution have on the surrounding environment and stream?
- Community/Traffic Disruption: How will the rehabilitation method impact traffic flow, business operations, and the community’s daily life?
- Estimated Construction Time: How long will it take to complete?
- Permitting Difficulty: The amount of difficulty and labor related to obtaining proper permits for the solution’s construction.
- Contractor Availability: The overall availability of relatively local contractors to install the solution?
We created the Culvert Rehab Products Evaluation Spreadsheet to help project owners evaluate options based on their site-specific priorities, requirements, and product specifications. Get your free copy here.
What Methods Are Available To Repair The Culvert?
Paving the invert is the first low-cost option to spot fix damaged areas in a culvert. While this can be effective in the short term, it provides minimal long-term structural benefit as it does not address the degrading structural capacity of the original pipe. While structurally adequate, replacing the structure is the Highest-Impact method, as it requires closing the roadway for the duration of the repair. This can be prohibitive in high traffic or extensive detours as the impact is too significant for commuter or emergency traffic. When entirely replacing the culvert, the project owner must also consider existing utility lines and how the removal of the structure may affect their continued service.
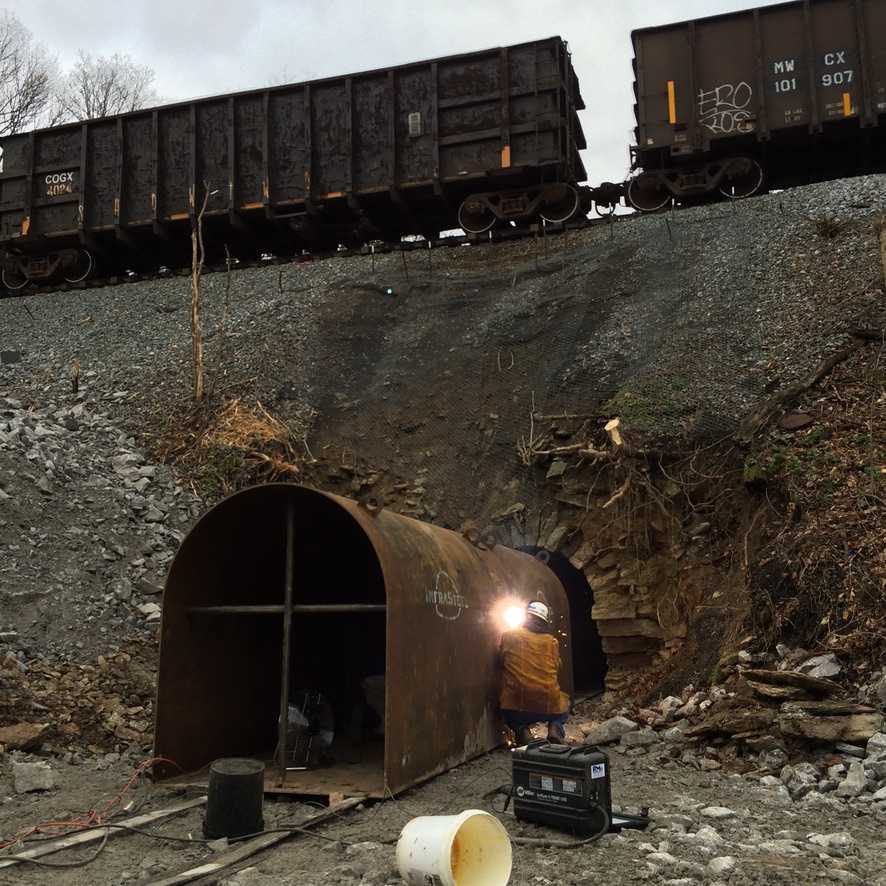
Slip-lining Of Culvert Structures Provides A Low Impact And Long-Term Repair Solution
Trenchless repair of the culvert pipe takes maximum advantage of the remaining usable structure so that the pipe is returned to its initial condition or better. These methods have less impact on the public since they can be done “inside” the host pipe without closing down the roadway. Trenchless repair is appropriate when the culvert loses its structural integrity but has not entirely failed or collapsed. A standard method to evaluate the Cost/Benefit of this repair method is conducting a Life Cycle Cost Analysis to determine how the upfront costs return value over time.
What Are The Most Common Trenchless Methods In Use Today?
- Cured In Place Liners use a flexible, resin-saturated tube that is pulled into the existing culvert. This is then expanded with water or air pressure and exposed to heat or ultraviolet light to stiffen. Curing of CIPP liners typically takes five to 30 hours, depending on the diameter and site conditions.
- Vinyl Wrap Liners use a specialized machine to install spirally wound vinyl material into the host pipe. The sections are fused as they pass through the machine and adhere to the contours of the host structure.
- Spray Lining occurs when the structure of the culvert is sprayed with a variety of liquid products. This reline method is typically less expensive but does not provide the structural support of other slip line methods. Spray lining materials can include polyurethane and cementitious materials.
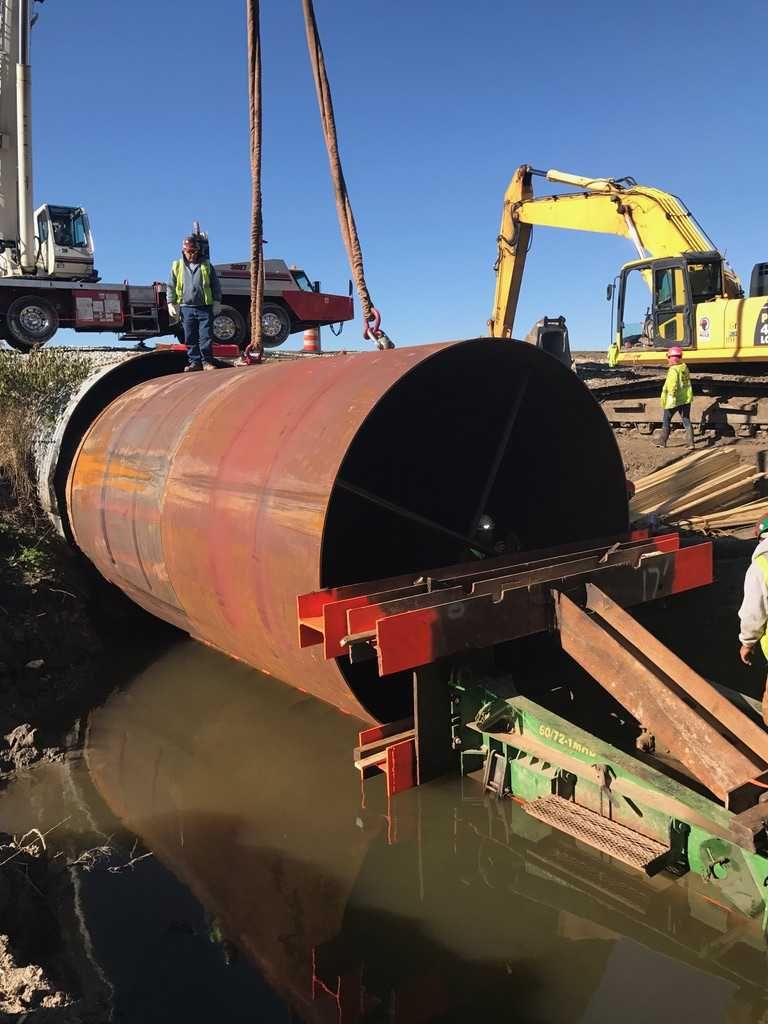
- Rigid Slip-Liners can consist of Smooth Wall Steel, HDPE, or RCP pipe. With this application, the new pipe is pushed into the existing structure and assumes all water displacement and load-bearing responsibility. Pressure grout is commonly used to seal the slip-liner in place. The application of rigid slip-liners typically provides the most extended service life and structural capacity of all trenchless repair methods.
In summary, it is critical to have a comprehensive understanding of which factors will affect the long-term performance of the culvert structure. This gives the project owner the best sense of which culvert repair method will be most appropriate for the site.
At Precision Pipe and Products, we developed our InfraSteel liner to satisfy market demand for a structural design with maximized flow characteristics and calculated design life. We engineer the design features required by the project owners by manufacturing site-specific liners that meet the needs of project owners. For more content relating to culverts and stormwater infrastructure, please visit us at www.INFRASTEEL.com or follow us on Facebook/Instagram/Twitter @InfraSteelUSA.








Leave A Reply